Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Consecutive submodeling with MAPDL pool#
- Problem description:
In this example, we demonstrate how to use MAPDL pool to perform a consecutive submodeling simulation with MAPDL and DPF.
- Analysis type:
Static Analysis
- Material properties:
Young’s modulus, \(E = 200 \, GPa\)
Poisson’s ratio, \(\mu = 0.3\)
- Boundary conditions (global model):
Fixed support applied at the bottom side
Frictionless support applied at the right side
- Loading:
Total displacement of -1 mm in the Y-direction at the top surface, ramped linearly over 10 timesteps
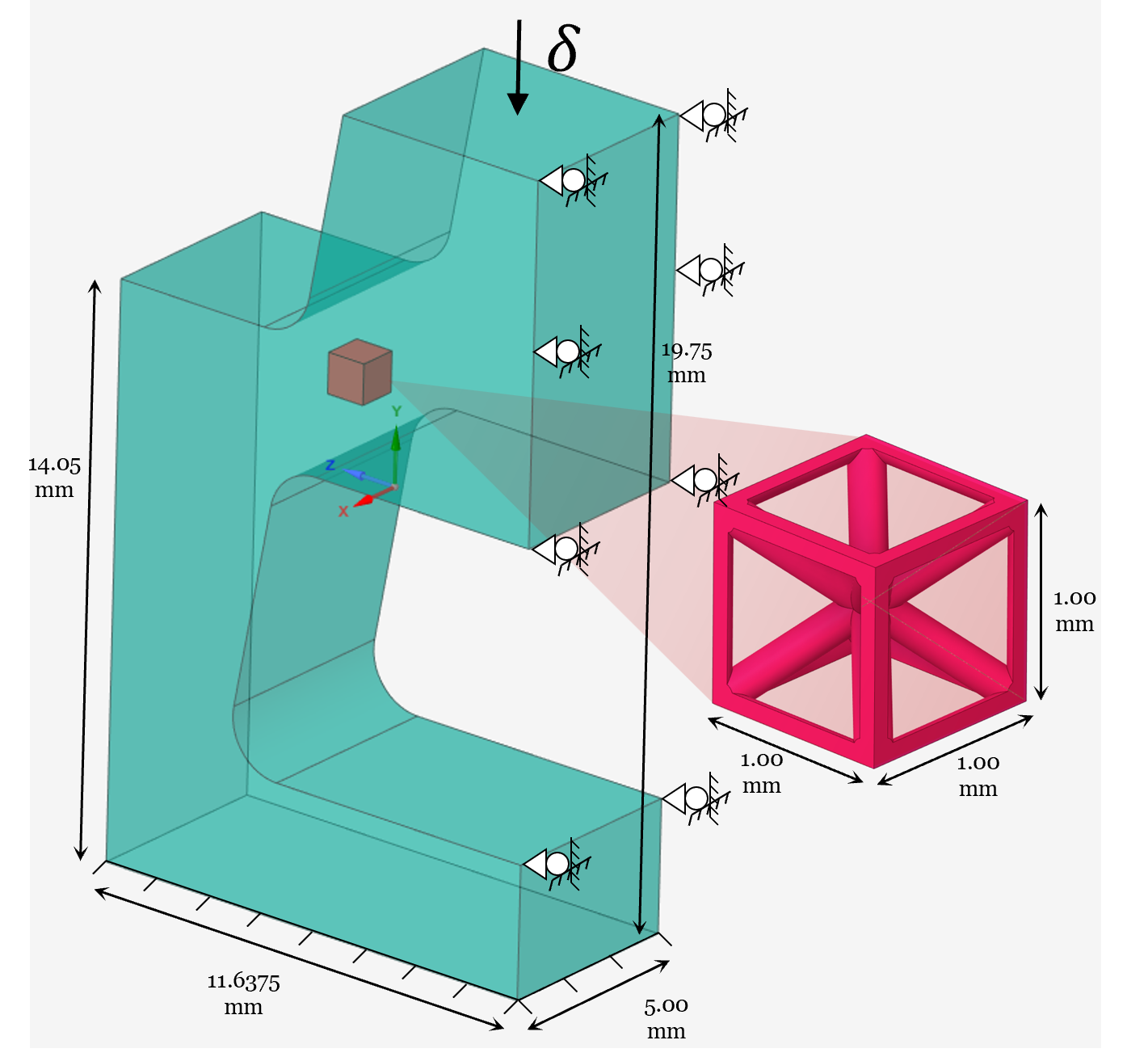
Problem sketch#
- Modeling notes:
At each timestep, the global model is solved with the specified boundary conditions; the resulting nodal displacements are interpolated to the boundary nodes of the local model, using the DPF interpolation operator. Those displacements are enforced as constraints to the local model, which is then solved, completing that timestep.
import os
from pathlib import Path
import shutil
import time as tt
from ansys.dpf import core as dpf
from ansys.mapdl.core import MapdlPool
from ansys.mapdl.core.examples.downloads import download_example_data
import numpy as np
Create directories to save the results#
folders = ["./outputs/mapdl-dpf/global", "./outputs/mapdl-dpf/local"]
for fdr in folders:
shutil.rmtree(fdr, ignore_errors=True)
Path(fdr).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# ##############################################################################
# Create a pool of MAPDL instances
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
# We use the ``MapdlPool`` class to create two separate instances: one dedicated to
# the global simulation and the other to the local simulation
port_0 = int(os.getenv("PYMAPDL_PORT_0", 21000))
port_1 = int(os.getenv("PYMAPDL_PORT_1", 21001))
is_cicd = os.getenv("ON_CICD", False)
n_cores = 2
if is_cicd:
mapdl_pool = MapdlPool(
port=[port_0, port_1],
)
else:
mapdl_pool = MapdlPool(2)
Creating Pool: 0%| | 0/2 [00:00<?, ?it/s]/__w/pyansys-workflows/pyansys-workflows/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/ansys/mapdl/core/launcher.py:1741: UserWarning: PyMAPDL couldn't detect MAPDL version, hence it could not verify that the provided connection mode 'grpc' is compatible with the current MAPDL installation.
warnings.warn(
Creating Pool: 50%|█████ | 1/2 [00:00<00:00, 1.93it/s]
Creating Pool: 100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:00<00:00, 3.19it/s]
Creating Pool: 100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:00<00:00, 2.90it/s]
Connect to DPF server#
We connect to a local or remote DPF server.
If you are working with a remote server, you might need to upload the RST
file before working with it.
Then you can create the DPF Model.
server_is_local = "DPF_PORT" not in os.environ
if server_is_local:
# Local server
dpf_server = dpf.server.start_local_server()
else:
# Remote server
dpf_server = dpf.server.connect_to_server(port=int(os.environ["DPF_PORT"]))
# ###############################################################################
# Set up global and local FE models
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
# We assign the instances to the local and global model, then use
# ``mapdl.cdread`` to load their geometry and mesh. Note the ``.cdb`` files
# include named selections for the faces we want to apply the boundary conditions and the loads.
# The function ``define_bcs`` defines the global model’s boundary conditions and applied loads.
# The function ``get_boundary`` is used to record the local model’s cut-boundary
# node coordinates as a ``dpf.Field`` which will be later used in the DPF interpolator input.
cwd = Path.cwd() # Get current working directory
# download example data
local_cdb = download_example_data(filename="local.cdb", directory="pyansys-workflow/pymapdl-pydpf")
global_cdb = download_example_data(
filename="global.cdb", directory="pyansys-workflow/pymapdl-pydpf"
)
mapdl_global = mapdl_pool[0] # Global model
mapdl_global.cdread("db", global_cdb) # Load global model
mapdl_global.cwd(cwd / Path("outputs/mapdl-dpf/global")) # Set directory of the global model
mapdl_local = mapdl_pool[1] # Local model
mapdl_local.cdread("db", local_cdb) # Load local model
mapdl_local.cwd(cwd / Path("outputs/mapdl-dpf/local")) # Set directory of the local model
def define_bcs(mapdl):
"""
Define boundary conditions and loading for the global model.
Parameters
----------
mapdl : Mapdl
MAPDL instance for the global model.
"""
# Enter PREP7 in MAPDL
mapdl.prep7()
# In the .cdb file for the global model the bottom, the right and the top faces
# are saved as named selections
# Fixed support
mapdl.cmsel("S", "BOTTOM_SIDE", "NODE") # Select bottom face
mapdl.d("ALL", "ALL")
mapdl.nsel("ALL")
# Frictionless support
mapdl.cmsel("S", "RIGHT_SIDE", "NODE") # Select right face
mapdl.d("ALL", "UZ", "0")
mapdl.nsel("ALL")
# Applied load
# Ramped Y‑direction displacement of –1 mm is applied on the top face over 10 time steps
mapdl.dim("LOAD", "TABLE", "3", "1", "1", "TIME", "", "", "0")
mapdl.taxis("LOAD(1)", "1", "0.", "1.", "10.")
mapdl.starset("LOAD(1,1,1)", "0.")
mapdl.starset("LOAD(2,1,1)", "-0.1")
mapdl.starset("LOAD(3,1,1)", "-1.")
mapdl.cmsel("S", "TOP_SIDE", "NODE") # Select top face
mapdl.d("ALL", "UY", "%LOAD%")
mapdl.nsel("ALL")
# Exit PREP7
mapdl.finish()
pass
def get_boundary(mapdl):
"""
Get the boundary node coordinates of the local model as a DPF field.
Parameters
----------
mapdl : Mapdl
MAPDL instance for the local model.
Returns
-------
dpf.Field
DPF field containing the coordinates of the boundary nodes of the local model.
"""
# Enter PREP7 in MAPDL
mapdl.prep7()
# In the .cdb file for the local model the boundary faces are saved as
# named selections
mapdl.nsel("all")
nodes = mapdl.mesh.nodes # All nodes
node_id_all = mapdl.mesh.nnum # All nodes ID
mapdl.cmsel("S", "boundary", "NODE") # Select all boundary faces
node_id_subset = mapdl.get_array("NODE", item1="NLIST").astype(int) # Boundary nodes ID
map_ = dict(zip(node_id_all, list(range(len(node_id_all)))))
mapdl.nsel("NONE")
boundary_coordinates = dpf.fields_factory.create_3d_vector_field(
num_entities=len(node_id_subset), location="Nodal"
) # Define DPF field for DPF interpolator input
nsel = ""
for nid in node_id_subset: # Iterate boundary nodes of the local model
nsel += "nsel,A,NODE,,{}\n".format(
nid
) # Add selection command for the node to the str (only for ploting)
boundary_coordinates.append(nodes[map_[nid]], nid) # Add node to the DPF field
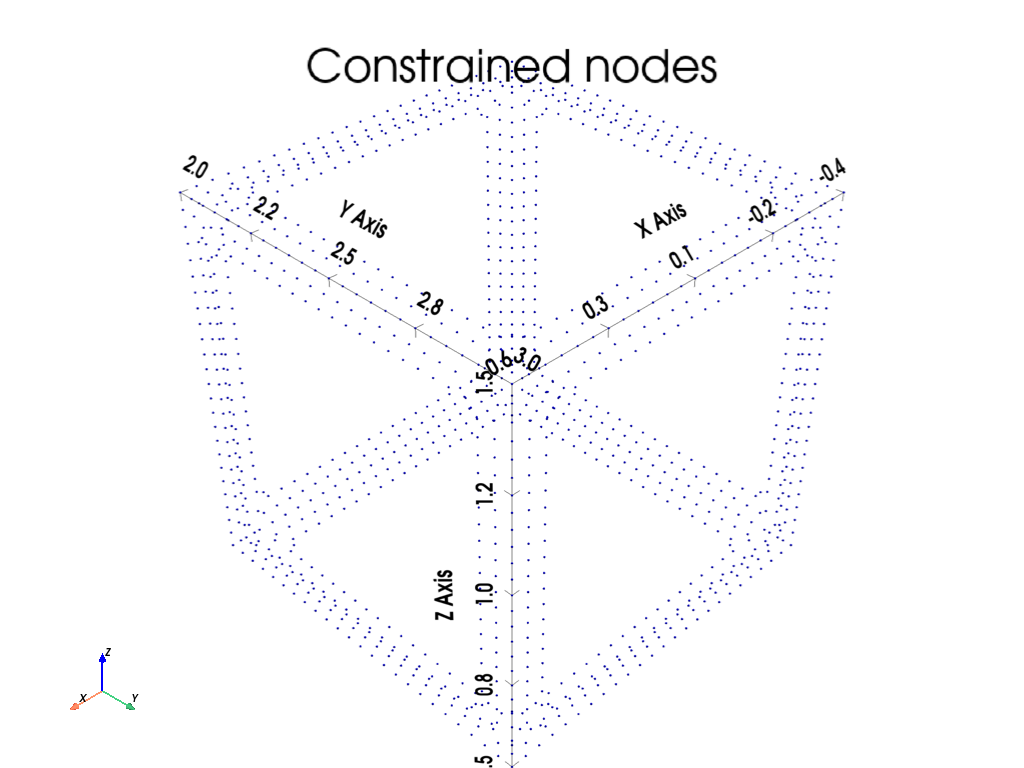
# Select all boundary nodes (only for ploting)
mapdl.input_strings(nsel)
# Plot boundary nodes of the local model
mapdl.nplot(background="w", color="b", show_bounds=True, title="Constrained nodes")
# Exit PREP7
mapdl.finish()
return boundary_coordinates
# Define the boundary conditions and the loading for the global model
define_bcs(mapdl_global)
# Get the DPF field with the boundary nodes of the local model
boundary_coords = get_boundary(mapdl_local)
Set up DPF operators#
We define two DPF operators: the first reads the displacement results from the global model,
and the second interpolates those displacements onto the boundary coordinates of the local
model. The DataSources class to link results with the DPF operator inputs.
def define_dpf_operators(n_cores):
"""
Define DPF operators for the global model.
Parameters
----------
n_cores : int
Number of cores used in the global model.
Returns
-------
dpf.Model
DPF model for the global model.
dpf.Operator
DPF operator to read nodal displacements from the global model.
dpf.Operator
DPF operator to interpolate displacements onto local model boundary coordinates.
"""
# Define the DataSources class and link it to the results of the global model
data_sources = dpf.DataSources()
for i in range(n_cores):
data_sources.set_domain_result_file_path(
path=Path(f"./outputs/mapdl-dpf/global/file{i}.rst"), key="rst", domain_id=i
)
global_model = dpf.Model(data_sources)
# Define displacement result operator to read nodal displacements
global_disp_op = dpf.operators.result.displacement()
# Connect displacement result operator with the global model's results file
global_disp_op.inputs.data_sources.connect(data_sources)
# Define interpolator to interpolate the results inside the mesh elements
# with shape functions
disp_interpolator = dpf.operators.mapping.on_coordinates()
return global_model, global_disp_op, disp_interpolator
def initialize_dpf_interpolator(
global_model,
local_bc_coords,
disp_interpolator,
):
"""
Initialize the DPF interpolator for the local model.
Parameters
----------
global_model : dpf.Model
DPF model for the global model.
local_bc_coords : dpf.Field
DPF field containing the coordinates of the boundary nodes of the local model.
disp_interpolator : dpf.Operator
DPF operator to interpolate displacements onto local model boundary coordinates.
"""
my_mesh = global_model.metadata.meshed_region # Global model's mesh
disp_interpolator.inputs.coordinates.connect(
local_bc_coords
) # Link interpolator inputs with the local model's boundary coordinates
disp_interpolator.inputs.mesh.connect(
my_mesh
) # Link interpolator mesh with the global model's mesh
def interpolate_data(timestep):
global_disp_op.inputs.time_scoping.connect(
[timestep]
) # Specify timestep value to read results from
global_disp = (
global_disp_op.outputs.fields_container.get_data()
) # Read global nodal displacements
disp_interpolator.inputs.fields_container.connect(
global_disp
) # Link the interpolation data with the interpolator
local_disp = disp_interpolator.outputs.fields_container.get_data()[
0
] # Get displacements of the boundary nodes of the local model
return local_disp
# Define the two DPF operators
global_model, global_disp_op, disp_interpolator = define_dpf_operators(n_cores)
Set up simulation loop#
We solve the two models sequentially for each loading step. First the global model is run producing a .rst results file. Then we extract the global displacements and use them to define cut-boundary conditions for the local model (an input string command will be used for faster excecution time).
def define_cut_boundary_constraint_template(local_bc_coords):
"""
Define template of input string command to apply the displacement constraints.
Parameters
----------
local_bc_coords : dpf.Field
DPF field containing the coordinates of the boundary nodes of the local model.
Returns
-------
str
Template of input string command to apply the displacement constraints.
"""
# Define template of input string command to apply the displacement constraints
local_nids = local_bc_coords.scoping.ids
# Get Node ID of boundary nodes of the local model
template = ""
for nid in local_nids:
template += (
"d,"
+ str(nid)
+ ",ux,{:1.6e}\nd,"
+ str(nid)
+ ",uy,{:1.6e}\nd,"
+ str(nid)
+ ",uz,{:1.6e}\n"
)
return template
def solve_global_local(mapdl_global, mapdl_local, timesteps, local_bc_coords):
"""
Solve the global and local models sequentially for each timestep.
Parameters
----------
mapdl_global : Mapdl
MAPDL instance for the global model.
mapdl_local : Mapdl
MAPDL instance for the local model.
timesteps : int
Number of timesteps to solve.
local_bc_coords : dpf.Field
DPF field containing the coordinates of the boundary nodes of the local model.
"""
# Enter solution processor
mapdl_global.solution()
mapdl_local.solution()
# Static analysis
mapdl_global.antype("STATIC")
mapdl_local.antype("STATIC")
constraint_template = define_cut_boundary_constraint_template(local_bc_coords)
for i in range(1, timesteps + 1): # Iterate timesteps
print(f"Timestep: {i}")
st = tt.time()
# Set loadstep time for the global model
mapdl_global.time(i)
# No extrapolation
mapdl_global.eresx("NO")
mapdl_global.allsel("ALL")
# Write ALL results to database
mapdl_global.outres("ALL", "ALL")
# Solve global model
mapdl_global.solve()
print("Global solve took ", tt.time() - st)
# Initialize interpolator
if i == 1:
initialize_dpf_interpolator(global_model, local_bc_coords, disp_interpolator)
# Read & Interpolate displacement data
local_disp = interpolate_data(timestep=i)
# Run MAPDL input string command to apply the displacement constraints
data_array = np.array(local_disp.data).flatten()
mapdl_local.input_strings(constraint_template.format(*data_array))
st = tt.time()
mapdl_local.allsel("ALL")
# Set loadstep time for the local model
mapdl_local.time(i)
# No extrapolation
mapdl_local.eresx("NO")
# Write ALL results to database
mapdl_local.outres("ALL", "ALL")
# Solve local model
mapdl_local.solve()
print("Local solve took ", tt.time() - st)
# Exit solution processor
mapdl_global.finish()
mapdl_local.finish()
Solve system#
n_steps = 10 # Number of timesteps
solve_global_local(mapdl_global, mapdl_local, n_steps, boundary_coords)
Timestep: 1
Global solve took 0.36406660079956055
Local solve took 0.5771195888519287
Timestep: 2
Global solve took 0.25287795066833496
Local solve took 0.499927282333374
Timestep: 3
Global solve took 0.2769629955291748
Local solve took 0.49933648109436035
Timestep: 4
Global solve took 0.24474716186523438
Local solve took 0.4763305187225342
Timestep: 5
Global solve took 0.2593114376068115
Local solve took 0.5030112266540527
Timestep: 6
Global solve took 0.24999022483825684
Local solve took 0.4992215633392334
Timestep: 7
Global solve took 0.24686980247497559
Local solve took 0.47165465354919434
Timestep: 8
Global solve took 0.26622462272644043
Local solve took 0.46829771995544434
Timestep: 9
Global solve took 0.2631680965423584
Local solve took 0.5000393390655518
Timestep: 10
Global solve took 0.2565324306488037
Local solve took 0.5031776428222656
Visualize results#
def visualize(mapdl):
# Enter post-processing
mapdl.post1()
# Set the current results set to the last set to be read from result file
mapdl.set("LAST")
# Plot nodal displacement of the loading direction
mapdl.post_processing.plot_nodal_displacement("Y", cmap="jet", background="w", cpos="zy")
# Exit post-processing
mapdl.finish()
# Plot Y displacement of global model
visualize(mapdl_global)
# Plot Y displacement of local model
visualize(mapdl_local)
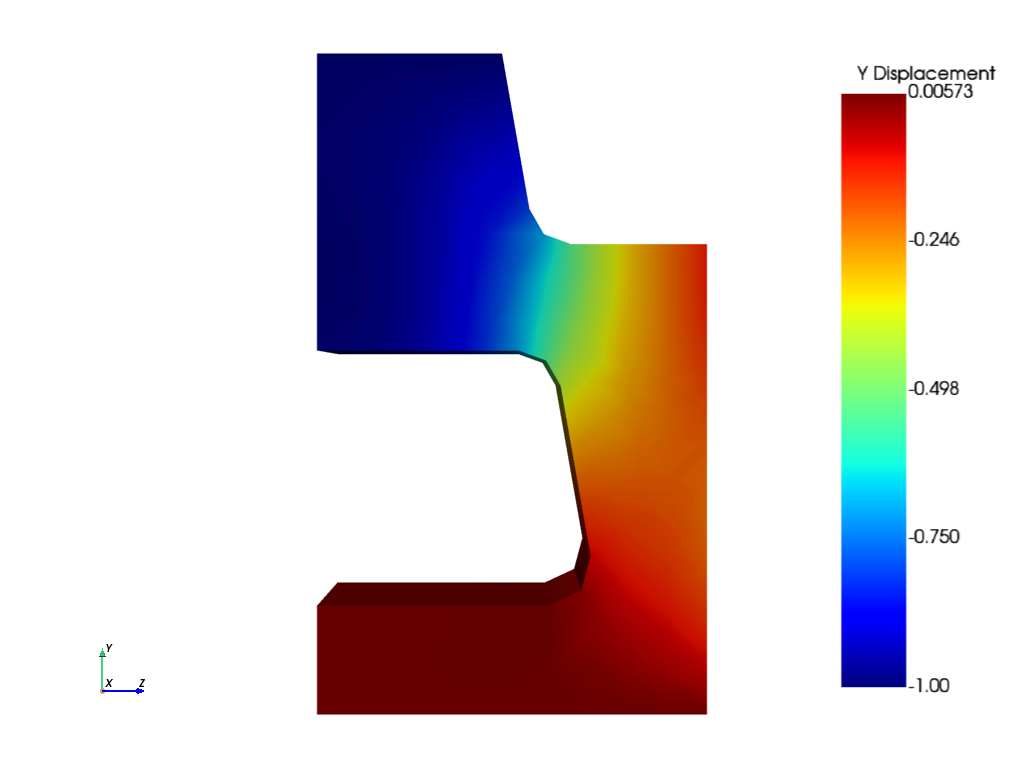
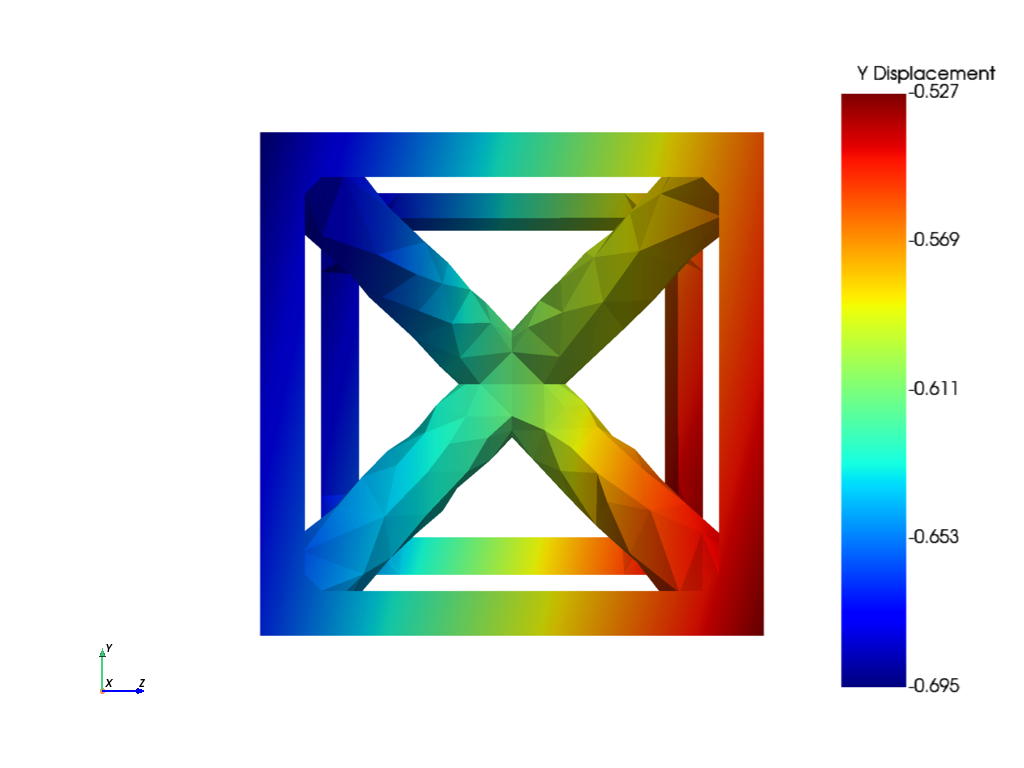
Exit MAPDL instances#
mapdl_pool.exit()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 19.691 seconds)

